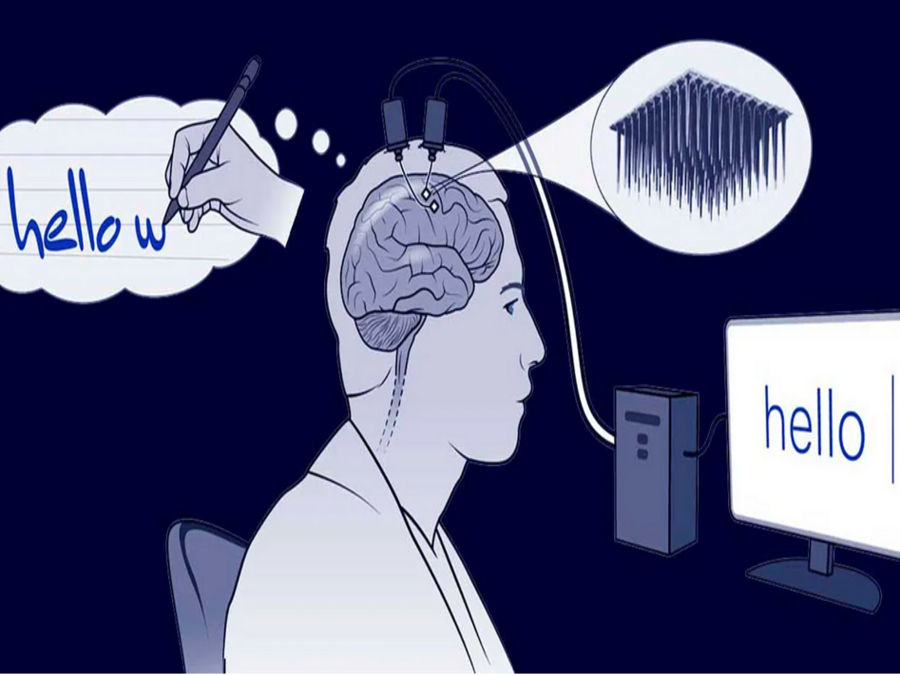
Brain-Machine Interface (BMI) Technologies
Neuralink stands out as a leading player, in the field of brain machine interfaces (BMI) with the goal of revolutionizing how humans interact with technology. The concept of a brain computer interface proposed by Neuralink has sparked a blend of enthusiasm and apprehension among the public.
Revolutionizing Human-Technology Interaction
The notion of merging minds with intelligence using BMI technology brings up various ethical and societal dilemmas. A key concern associated with this technology is the potential for privacy breaches and the risk of manipulation by entities such as governments or corporations. The disconcerting idea of others being able to access and interpret our thoughts underscores the importance of establishing ethical guidelines to govern the utilization of such advanced technologies.
Ethical Dilemmas: Privacy and Autonomy at Stake
Neuralinks ambitious goals go beyond applications to enhancing abilities within the realm of advancing artificial intelligence. Elon Musk envisions a future where individuals can communicate their sensations, emotions and memories through targeted stimulation of neurons or brain regions thereby expanding potential in a rapidly changing technological landscape. However, this vision also raises worries about loss of autonomy and susceptibility to influences as our understanding of the brain progresses.
Beyond Medicine: The Broader Implications of Enhancing Human Capabilities
The integration of BMI technology with the brain opens up a range of possibilities from advancements in healthcare, to immersive experiences. The allure of using technology, for healing and virtual world creation is attractive. It also carries the risk of misuse leading to harm, dependency and isolation. The fine line between the benefits and drawbacks of BMI technology underscores the importance of evaluating its impact, on society.
Promising Prospects: From Treatment to Total Immersion
Brain Machine Interfaces (BMIs) have the potential to transform how we treat disorders and physical disabilities offering a ray of hope in areas where traditional medicine falls short. They could potentially help manage conditions such, as Parkinsons disease, epilepsy and spinal cord injuries by using interventions to restore lost functions.
Apart from their applications BMIs could pave the way for an era of collaboration between humans and machines. This collaboration could enhance our experiences and cognitive abilities creating opportunities for improved learning environments where knowledge is directly integrated into our brains. Additionally imagine experiences that feel incredibly real providing an escape authentic as physically being there. All made possible through neural interfaces. These possibilities hold the promise of improving our quality of life and unlocking levels of human potential.
Potential Perils: Risks and Ethical Concerns
However along with the promise of this technology comes risks. One major concern is the potential for inducing pain or manipulating sensations, which could be abused in experiments or forms of manipulation that may border on torture. The manipulation of experiences also raises concerns about addiction or dependency on states of happiness or escapism. Similar, to challenges posed by substance abuse but potentially more pervasive and difficult to tackle.
Furthermore as BMIs enable virtual experiences there is a risk of exacerbating social disconnection. If people begin to prioritize environments, over face to face interactions it may lead to increased feelings of loneliness affecting connections and community engagement. This shift could greatly impact well being potentially causing rates of depression or anxiety as, in person communication is replaced by virtual options.
Governance and Responsibility: Societal Impacts and Ethical Governance
The diverse public opinion about Neuralink and BMI technology underscores a nuanced interplay of hopes and fears that surround the merging of human brains with computers. Others see a future in which humans can achieve immortality through uploading their minds; however, some question the consequences of such deep technological integration. The ethical and social implications of BMI technologies are at the heart of debates on their development and use.
It is therefore important for Neuralink to engage in discussions that go beyond technological advancements into more societal impacts associated with joining human brains with artificial intelligence. It is crucial to address the questions relating to ethics, privacy, or autonomy related to BMI technologies so as to open up a future where innovation works hand in hand with human values for good living.
These broader implications highlight balanced approach that must be taken towards designing and employing BMI technology. In navigating this new land, the boundary between enhancing life and posing dangers becomes obscure underlining need not only for what is possible but also what is right.
It is highly important that policymakers, technologists and ethicists collaborate in setting up rules which protect individuals and the society. This requires putting in place safeguards against misuse, standards for user consents and laws on equitable distribution of such technologies. Public participation should matter a lot while making policies that reflect societal values and preferences to ensure as BMI technologies do not debase but contribute positively to the human experience.
The final thought on the effects of Neuralink and Brain-Machine Interface Technologies is that they are numerous and complicated. On one hand, these merging of human brains with AI can promise great benefits. On the other hand, there is a need to consider this new direction carefully and even with some foresight to anticipate and avoid possible challenges. It should be emphasized, however, that the development of BMI technologies can be ethical if we concentrate not only on technological advancement but also on human welfare.
Sources:
- https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9462223
- https://arxiv.org/abs/1805.00789
- https://wiki.bitsathy.ac.in/wiki/NEWSLETTER:Budbringer#Volume_06