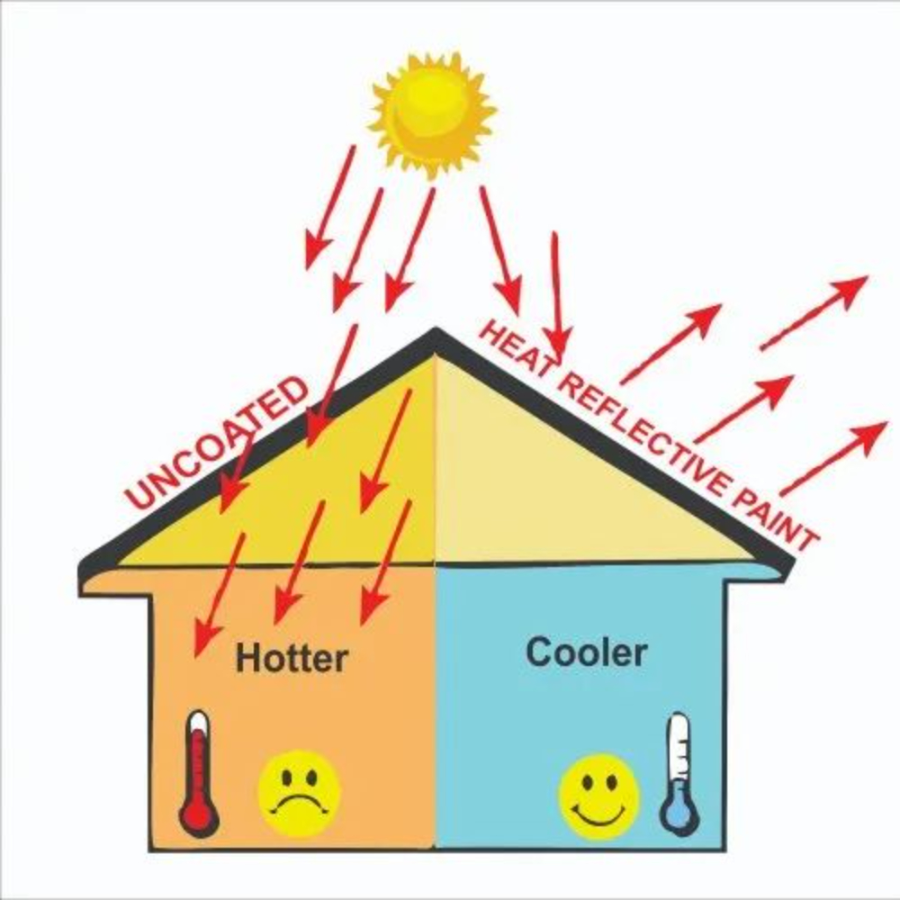
Reflective Solar cooling paint
Designed to mitigate heat absorption on surfaces exposed to sunlight that utilizes reflective properties to reduce solar heat gain. This is applied as a paint coating on various surfaces.
Descriptions of cooling paint:
- Composition:
Cooling paint typically consists of advanced reflective pigments and additives that contribute to its heat-reflective properties. These formulations are designed to effectively repel a significant portion of solar radiation.
- Reflective Properties:
The key feature of cooling paint is its high solar reflectance. This means it can reflect a substantial amount of sunlight away from the painted surface. The paint acts as a barrier against the absorption of solar heat, keeping the coated area cooler than it would be with traditional paints.
- Infrared Reflectivity:
In addition to reflecting visible light, cooling paint often possesses high infrared reflectivity. This capability allows it to bounce back infrared radiation, which is responsible for the majority of heat gain on surfaces exposed to the sun.
- Thermal Emittance:
Cooling paints also exhibit high thermal emittance. This means they efficiently release absorbed heat, preventing the buildup of thermal energy on the painted surface. This feature is crucial for maintaining lower temperatures even during prolonged sun exposure.
- Application Process:
Cooling paint is applied like conventional paints, making it versatile for various surfaces such as roofs, walls, and pavements. Proper surface preparation is essential to ensure good adhesion and longevity of the cooling effect.
- Energy Efficiency:
By reducing solar heat absorption, cooling paint contributes to enhanced energy efficiency in buildings. This can result in decreased reliance on air conditioning systems, leading to lower energy consumption and utility costs.
- Environmental Benefits:
Cooling paints are often formulated to be environmentally friendly. They contribute to sustainability efforts by reducing the demand for energy-intensive cooling methods, thereby lowering carbon emissions and promoting a greener approach to building maintenance.
- Durability:
High-quality cooling paints are designed to withstand weathering, UV radiation, and other environmental factors. This durability ensures a longer lifespan for the painted surfaces, maintaining their reflective and cooling properties over time.
Materials used in cooling paint
Cooling paint formulations often involve specific materials that contribute to their reflective and heat-dissipating properties. Here are some common materials used in cooling paint along with brief descriptions of their roles:
- Reflective Pigments: These are typically white or highly reflective pigments such as titanium dioxide. They play a crucial role in reflecting a significant portion of sunlight, reducing the absorption of solar radiation by the painted surface.
- Infrared Reflective Additives: Certain additives are included to enhance the paint’s ability to reflect infrared radiation. These additives, often in the form of particles or coatings, contribute to preventing the penetration of heat into the painted material.
- Microspheres: Microspheres are tiny hollow spheres filled with gas. When included in cooling paint formulations, they can improve thermal insulation by reducing the transfer of heat. They also contribute to the lightweight nature of the paint.
- Binders: Binders are essential components that hold the paint together and adhere it to the painted surface. They play a role in the overall durability and longevity of the cooling paint.
- UV-Blocking Agents: These agents help protect the paint from the degrading effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation, ensuring that the cooling paint maintains its reflective and cooling properties over an extended period.
- Ceramic Microspheres: Ceramic microspheres are small particles made from ceramics. When incorporated into cooling paint, they contribute to its insulating properties and can enhance the paint’s resistance to weathering.
- Phase Change Materials (PCMs): Some advanced cooling paints may incorporate phase change materials that can absorb and release heat during phase transitions. This can provide an additional mechanism for temperature regulation.
- Nano-Reflective Particles: Nano-sized reflective particles, such as nano-titanium dioxide, can be used to further enhance the reflective properties of cooling paint. Their small size allows for improved dispersion within the paint matrix.
- Polymer Matrices: Polymers are often used as a matrix to hold the various components of the cooling paint together. They can contribute to the flexibility, adhesion, and overall performance of the paint.
- Anti-Fungal and Anti-Algal Agents: To prevent the growth of fungi and algae on painted surfaces, anti-fungal and anti-algal agents are sometimes included. This helps maintain the aesthetic appeal and longevity of the cooling paint.
What happens if cooling paint is not applied?
If cooling paint is not applied, several consequences related to heat absorption and elevated surface temperatures may occur, depending on the specific context and application.
- Without cooling paint, surfaces exposed to sunlight, such as roofs and walls, may absorb more solar radiation. This can lead to higher surface temperatures, causing indoor spaces to become warmer. Consequently, buildings may rely more on air conditioning systems, resulting in increased energy consumption and higher utility bills.
- Buildings without cooling paint may place a greater strain on cooling systems, potentially leading to more frequent breakdowns, higher maintenance costs, and an increased risk of system failures during peak demand periods.
Conclusion
Cooling paint is a specialized type of paint designed to mitigate heat absorption on surfaces exposed to sunlight. It achieves this through a combination of reflective pigments, infrared-reflective additives, and other materials that collectively reduce the impact of solar radiation. Additionally, it has environmental benefits by decreasing overall carbon emissions and aiding in the mitigation of the urban heat island effect. The versatility of cooling paint allows it to be applied to various surfaces, such as roofs and walls, making it adaptable to different settings. However, challenges such as the initial cost, application considerations, and variations in effectiveness based on environmental conditions need to be carefully considered. Overall, cooling paint represents an innovative solution for creating more comfortable and sustainable living and working environments, particularly in regions with high sun exposure.
Source
- https://www.rawlinspaints.com/blog/the-benefits-of-heat-reflective-roof-paints/